Starliner Astronauts May Return on Delayed Crew-9 Mission
According to reports, NASA is weighing Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams’ return on a SpaceX Dragon.
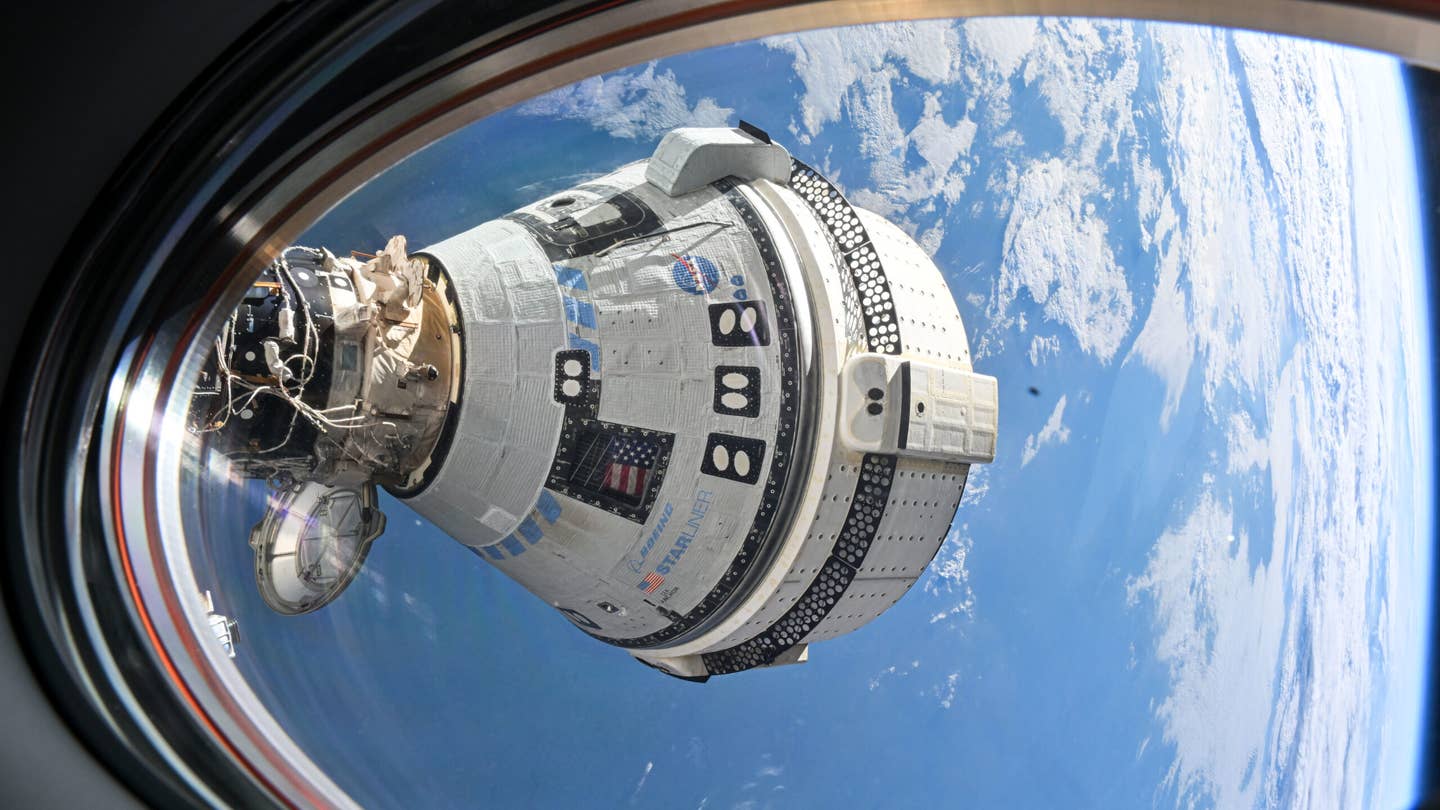

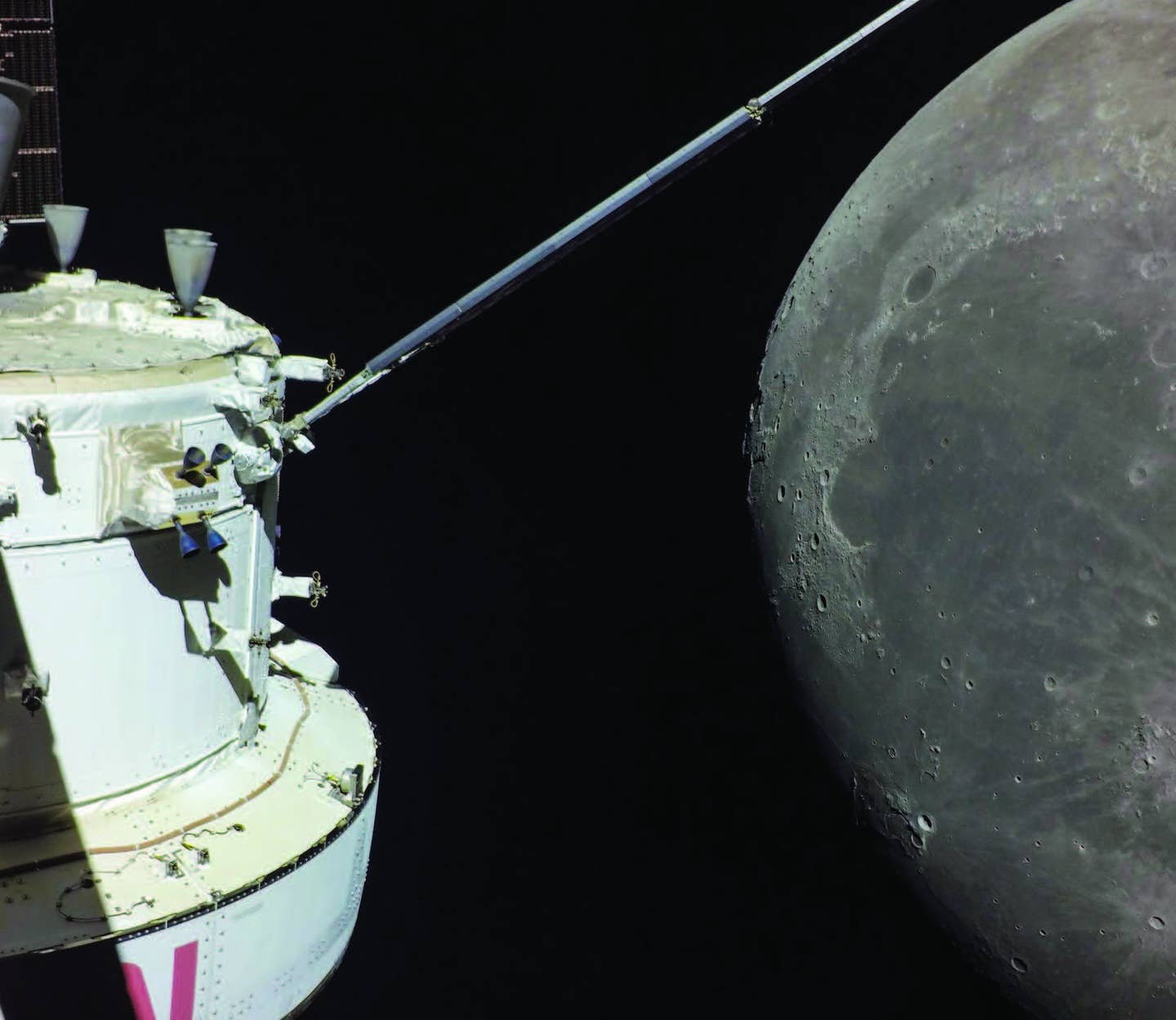
Boeing’s Starliner has been docked to the International Space Station’s Harmony module since June 6. [Courtesy: NASA]
NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams, who have been on the International Space Station for two months despite an intended eight-day stay, may not come home on the Boeing-built capsule that brought them there. But the alternative may not reach them until September.
NASA and Boeing are in the midst of the inaugural crew flight test (CFT) of Starliner, a semireusable vessel to the ISS under contract for agency service missions as soon as next year. But en route to the orbital laboratory, the spacecraft suffered several anomalies that have led teams to keep it on the ISS for further testing.
A preflight readiness review, during which crews would make a determination on Starliner’s return date, was expected last month but has since been pushed back, with no updates provided since last week.
NASA and Boeing last held a meeting to discuss Starliner’s issues with the media on July 25 and have insisted that the Boeing capsule will return the astronauts to Earth. However, as first reported by Ars Technica and confirmed by FLYING, it appears the space agency is considering enlisting SpaceX’s Dragon.
“NASA is evaluating all options for the return of agency astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams from the International Space Station as safely as possible,” a NASA spokesperson told FLYING. “No decisions have been made and the agency will continue to provide updates on its planning.”
The statement is a marked shift from the agency’s tone thus far, which has been adamant about Starliner safely returning Wilmore and Williams.
While SpaceX’s Dragon is not mentioned by name, it is the only vehicle in NASA’s ISS Commercial Crew rotation program. Steve Stich, who manages the Commercial Crew program, previously said that there were no discussions between the agency and SpaceX about using Dragon as an alternative. However, NASA in July issued a task award for SpaceX to study flying Dragon with six passengers, rather than the typical four.
In theory, the spacecraft could accommodate the four-person crew of SpaceX’s upcoming Crew-9 mission in addition to Wilmore and Williams. NASA is reportedly also considering flying Crew-9 with two crewmembers, leaving room for the two astronauts on the ISS.
The problem, though, is that Crew-9 on Tuesday was delayed from August 18 to September 24 to give Starliner teams more time to finalize a return plan.
Multiple independent sources also told Ars Technica that Starliner’s onboard flight software is not currently capable of completing an automated undocking from the ISS—despite the capsule completing that maneuver during an uncrewed flight test in 2022—and could take nearly a month to be updated.
If the report is accurate, the software issue would compound Starliner’s existing problems, the most consequential being a set of misfiring thrusters.
Five reaction control system (RCS) thrusters on the spacecraft’s service module fired at lower levels than expected during the trip to the orbital laboratory. The thrusters have been tested on orbit and are now operating at or near expected levels, according to NASA.
But the agency continues to wrap up ground testing at White Sands Test Facility in New Mexico, where an identical thruster is being evaluated. It appears crews do not yet have full confidence in the thrusters’ performance, as evidenced by the delay to the flight readiness review.
NASA continues to tout safety as its highest priority for the CFT, but there are certainly some politics at play.
On July 25, Stich said NASA would like to see Starliner return Wilmore and Williams during the CFT, implying that another crewed test could be required for certification if it doesn’t. The CFT is intended to be the final test flight, but Stich previously acknowledged that certification could take longer than originally expected.
Boeing last week released a statement appearing to publicly pressure NASA, reiterating its confidence in the vessel as evidenced by the extensive testing that has been performed since it docked at the ISS.
Already, Starliner’s inaugural service mission has been delayed from February to August 2025, adding to the almost decade of setbacks the program has suffered. Adding to the headache, Boeing has reportedly spent $1.6B on Starliner so far.
The manufacturer has plenty of incentive to push for Wilmore and Williams’ return on the spacecraft. But at the same time, a failed mission would likely torpedo the program, leaving stakeholders with a difficult decision.
Like this story? We think you'll also like the Future of FLYING newsletter sent every Thursday afternoon. Sign up now.

Sign-up for newsletters & special offers!
Get the latest FLYING stories & special offers delivered directly to your inbox