Pointers for Packing Your First Flight Bag
Here’s what you need to begin that special aviation journey.

FLYING has a few suggestions for what to put in your flight bag so you are prepared for the best training
experience possible. [iStock]
While your pilot certificate feels like the most valuable thing in your possession—you would be correct. But you’ll need other tools in order to use it.
It takes a lot of personal equipment to learn to fly. It’s frustrating when you don’t have something you need—especially if no one told you that you’d need it. You may have noticed that pilots carry specialized gear bags, referred to as “flight bags.” They are designed with padded pockets for delicate items, such as headsets and tablets, along with multiple straps in which to store items so that they can be located readily in flight.
FLYING has a few suggestions for what to put in your flight bag so you are prepared for the best training experience possible.
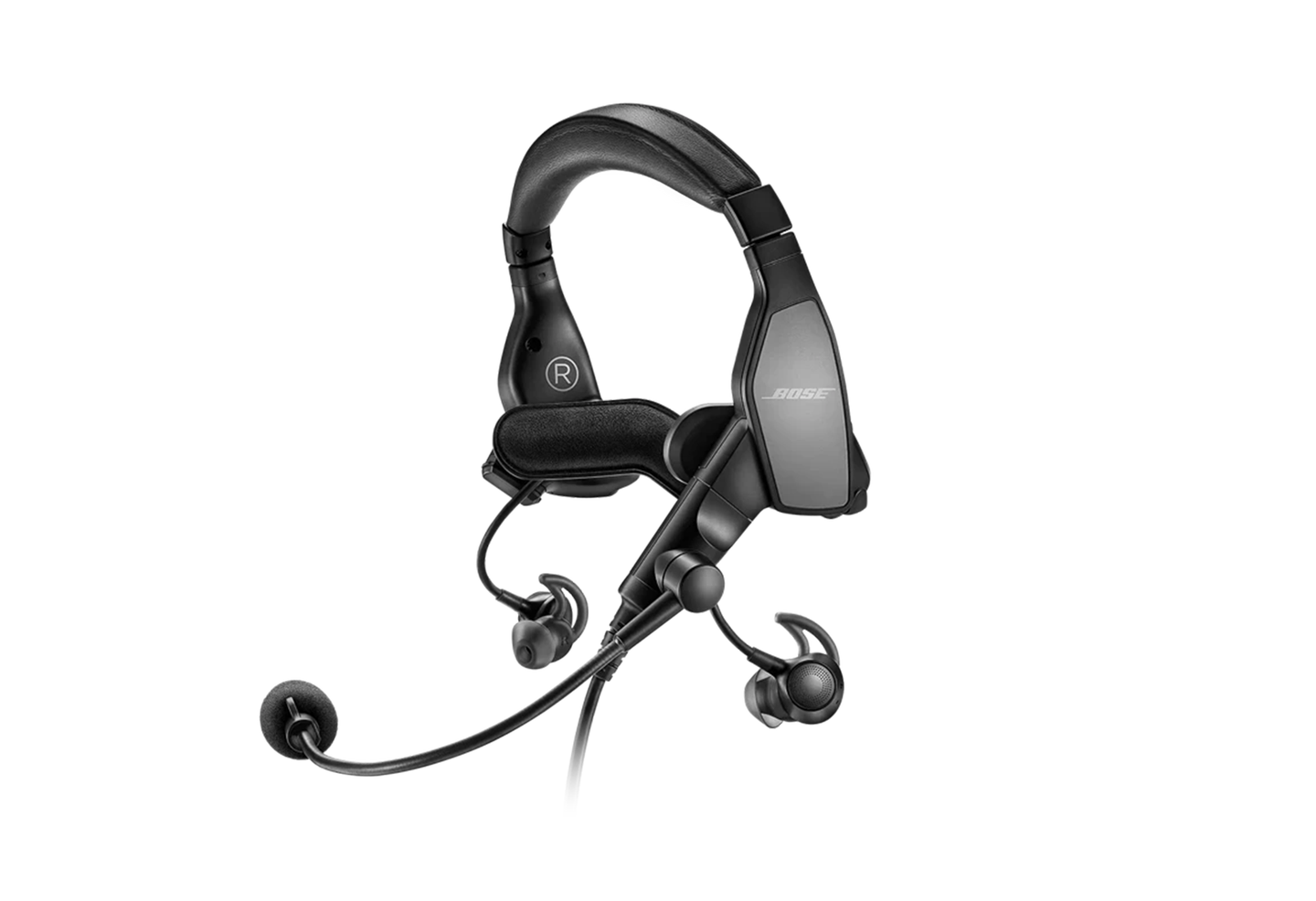
Headset
Aviation can be loud. Hearing loss can be a common affliction among pilots, so protect what you have. An aviation headset, preferably one with a noise-canceling function, should be your first purchase to put in your bag. In fact, the padded pocket of most bags fits this purpose precisely. If the headset uses batteries, always make sure you carry spares and keep them in the original packing until use. This protects them from interacting with metal (like keys or clips on pens), which can lead to electric arcing and fire.
Flashlight
An aviation flashlight should have a white lens and at least one colored lens—be it green, red, blue, or amber—to protect your night vision. Some pilots carry multiple flashlights. For example, one could be an L-shaped, military-issue C-cell battery strapped to a shoulder harness so it projects on the instrument panel during night flights.
Kneeboard
A kneeboard is like a lap desk you use in the airplane. Make sure it can be secured to your leg and is stable. Also, ensure it does not get in the way of the yoke or stick when installed on your leg. It should have room for your notebook or tablet and a means to hold writing implements.
Charts and Chart Supplement
You may use ForeFlight or another app in the aircraft on a tablet, but you may find the paper versions of this information—in the form of charts—come in handy. Paper doesn’t break when you drop it on a hard surface like the ramp, and you can read paper charts easily in direct sunlight. Sectionals and terminal area charts (TACs) can also be turned into sunshades if you need them. Make sure they are current if you intend to use them in the aircraft.
Fuel Strainer/Pipette or Gauge
You will use these tools during every preflight to check the fuel for impurities (a strainer) and the actual amount in the tanks (a pipette or gauge). Many flight schools have these on board the aircraft, but they tend to go missing. Make sure you put your name on yours and that the pipette/gauge is the correct one to use for the fuel tanks on the airplane you fly.
POH/AFM
There is supposed to be a pilot’s operating handbook (POH) or aircraft flight manual (AFM) aboard your training airplane. It covers the “O” in the “ARROW” mnemonic pilots use to recall the necessary documentation for the aircraft, in fact, because it includes the “operating limitations” referenced by that letter. In addition to the one found in the aircraft, you should have a POH/AFM of your own for reference. You will be using this book for every flight to determine takeoff and landing distance, fuel burn, etc.
for use are printed on it. [Courtesy: ASA]
E6-B Flight Computer
The flight computer is a must-have. They come in an electronic form (think calculator on steroids) or the mechanical E6-B, which is a circular slide rule and looks intimidating until you realize the instructions for use are printed on it. For primary pilots, I like the manual E6-B because the wind side helps with visualization of crosswinds and learning about VORs. You will use the E6-B during your knowledge test. Although there are apps for E6-Bs, you won’t be allowed to use your smartphone during the knowledge test, so get used to using something else.
Syllabus
Bring the syllabus with you to every lesson. Every. Lesson. Find an instructor who knows how to use one and will use one. It’s the best way to keep your training on course.
Multitool
This is a “just-in-case” device. You may need a tool to adjust your headset fit, trim a piece of rope, open a bottle of oil, or reseat a screw if the FBO and/or school policies permit.
Notebook and Pen
There is a lot of note taking as a pilot. You should make notes during the pre-lesson and post-lesson briefing with your instructor. You will also be writing down things in the cockpit—for example, the information from the automated weather. While there are many who choose to record information electronically, you may find paper more expedient as it does not require batteries and can be used as fire fuel in an emergency situation. Make sure you have several writing implements as well.
This feature first appeared in the March 2024/Issue 946 of FLYING’s print edition.

Sign-up for newsletters & special offers!
Get the latest FLYING stories & special offers delivered directly to your inbox